RefElemData type
RefElemData contains the following fields
element_type::AbstractElemShape: element shape.Line, Tri, Quad, Hex, Wedge, Pyr, Tetcurrently supported.approximation_type: approximation type. Defaults toPolynomial(), butSBP()is also supported (see RefElemData based on SBP finite differences).Nfaces: number of faces on a given type of reference element.fv: list of vertices defining faces, e.g.,[1,2], [2,3], [3,1]for a triangleFmask: indices of interpolation nodes which lie on the facesVDM: the generalized Vandermonde matrix, a square matrix whose columns are $V_{ij} = \phi_{j}(x_i}$, where $\phi_j$ are orthonormal basis functions and $x_i$ are interpolation points.rst::NTuple{Dim, ...}: tuple of vectors of lengthN_p, each of which contains coordinates of degree $N$ optimized polynomial interpolation points.rstq::NTuple{Dim, ...},wq,Vq: tuple of volume quadrature points, vector of weights, and quadrature interpolation matrix. Each element ofrstqandwqare vectors of length $N_q$, andVqis a matrix of size $N_q \times N_p$.N_{\rm plot}: the degree which determines the number of plotting points $N_{p,{\rm plot}}$.rstp::NTuple{Dim, ...},Vp: tuple of plotting points and plotting interpolation matrix. Each element ofrstpis a vector of length $N_{p,{\rm plot}}$, andVpis a matrix of size $N_{p,{\rm plot}} \times N_p$.rstf::NTuple{Dim, ...},wf,Vf: tuple of face quadrature points, weights, and face interpolation matrix. Each element ofrstfandwfare vectors of length $N_f$, andVfis a matrix of size $N_f \times N_p$.nrstJ::NTuple{Dim, ...}: tuple of outward reference normals, scaled by the face Jacobian. Each element is a vector of length $N_f$.M: mass matrix computed using quadrature. Size $N_p \times N_p$Pq: quadrature-based $L^2$ projection matrix. Size $N_p \times N_q$.Drst::NTuple{Dim, ...},LIFT: differentiation and lifting matrices. Differentiation matrices are size $N_p \times N_p,$ while lift matrices are size $N_p\times N_f$.
This list is incomplete; other fields are stored or accessible but currently only used for internal computations.
Mass, differentiation, lifting, and interpolation matrices can be specialized. For example, these matrices are dense Matrix{T} type for lines and triangles, but could also be stored as sparse matrices for quadrilaterals and hexahedra.
Setting up rd::RefElemData
The struct rd::RefElemData contains data for a given element type. All common reference elements are supported: Line, Tri, Quad, Tet, Pyr, Wedge, and Hex.
To initalize a RefElemData, just specify the element type and polynomial degree.
N = 3
# 1D elements
rd = RefElemData(Line(), N)
# 2D elements
rd = RefElemData(Tri(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Quad(), N)
# 3D elements
rd = RefElemData(Tet(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Pyr(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Wedge(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Hex(), N)Specifying different quadrature rules.
By default, RefElemData initializes volume and surface quadrature rules to be the minimum rules which exactly integrate the unweighted volume and surface mass matrices. If different quadrature rules are desired, they can be specified as follows:
N = 3
# create degree N tensor product Gauss-Lobatto rule
r1D, w1D = gauss_lobatto_quad(0, 0, N)
rq, sq = vec.(StartUpDG.meshgrid(r1D))
wr, ws = vec.(StartUpDG.meshgrid(w1D))
wq = @. wr * ws
rd = RefElemData(Quad(), N; quad_rule_vol = (rq, sq, wq),
quad_rule_face = (r1D, w1D))This results in a DG spectral element method (DG-SEM) discretization, with a diagonal lumped mass matrix and differentiation matrices which satisfy a summation-by-parts property.
By default, RefElemData is constructed for a nodal basis (in order to facilitate curved meshes, connectivity, etc). The interpolation nodes are computed using an interpolatory version of the warp-and-blend procedure.
While specifying the quadrature rule changes the discretization, it is not reflected in the RefElemData type and thus cannot be specialized on. The following constructors produce RefElemData where the quadrature structure is reflected in the type parameters:
rd = RefElemData(Hex(), Polynomial(TensorProductQuadrature(quad_nodes(Line(), N+1)), N)) # tensor product quadrature rules
rd = RefElemData(Quad(), Polynomial{Gauss}(), N) # (N+1)^d point tensor product Gauss quadratureRefElemData based on SBP finite differences
It is also possible to construct a RefElemData based on both traditional finite difference SBP operators and multi-dimensional SBP finite difference operators. The traditional finite difference SBP operators are built using SummationByPartsOperators.jl. The multi-dimensional SBP operators utilize nodes constructed by Tianheng Chen and Chi-Wang Shu, Ethan Kubatko, and Jason Hicken.
Some examples of traditional finite difference SBP operators on tensor product domains:
using StartUpDG
using SummationByPartsOperators # this package must be loaded to enable extension
D = derivative_operator(MattssonNordström2004(),
derivative_order=1, accuracy_order=N+1,
xmin=-1.0, xmax=1.0, N=20)
rd = RefElemData(Line(), D)
rd = RefElemData(Quad(), D)
rd = RefElemData(Hex(), D)Some examples of multi-dimensional SBP operators:
N = 3
rd = RefElemData(Quad(), SBP(), N) # defaults to SBP{TensorProductLobatto}
rd = RefElemData(Quad(), SBP{TensorProductLobatto}(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Hex(), SBP(), N) # defaults to SBP{TensorProductLobatto}
rd = RefElemData(Hex(), SBP{TensorProductLobatto}(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Tri(), SBP(), N) # defaults to SBP{Kubatko{LobattoFaceNodes}}
rd = RefElemData(Tri(), SBP{Hicken}(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Tri(), SBP{Kubatko{LobattoFaceNodes}}(), N)
rd = RefElemData(Tri(), SBP{Kubatko{LegendreFaceNodes}}(), N) Quadrature rules of both degree 2*N-1 (up to N = 6) and 2*N (up to N = 4) are supported on triangles. For Line, Quad, and Hex elements, RefElemData(..., SBP(), N) is the same as the RefElemData for a DG-SEM discretization, though some fields are specialized for the SBP type. These SBP-based RefElemData objects can also be used to initialize a mesh (for example, md = MeshData(uniform_mesh(rd.element_type, 4)..., rd)).
On triangles, we have the following SBP types with the following properties:
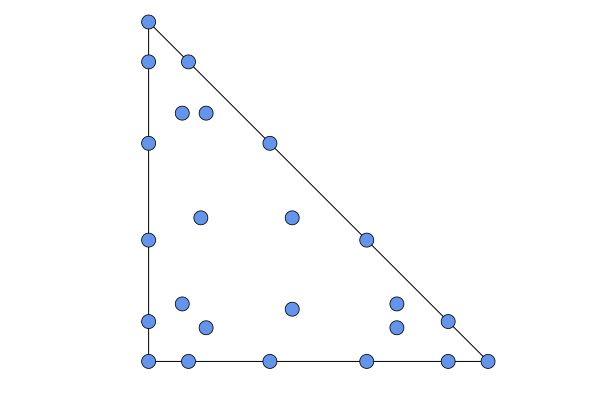
SBP{Kubatko{LobattoFaceNodes}}: degree2N-1accurate quadrature rules withN+2Lobatto nodes on each face. Nodes forN=4:
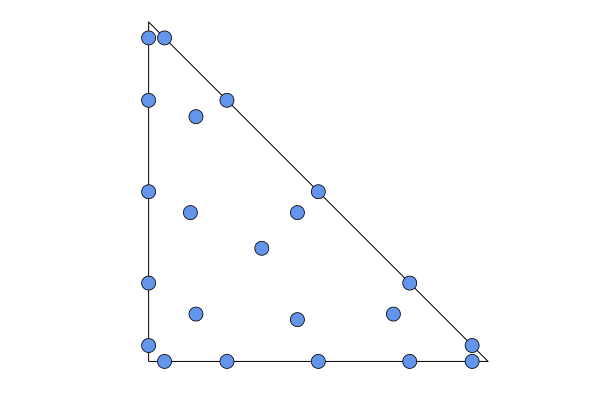
SBP{Kubatko{LegendreFaceNodes}}: degree2N-1accurate quadrature rules withN+1Legendre nodes on each face. ForN = 1,...,4, these are the same as the nodes constructed by Chen and Shu. Nodes forN=4:
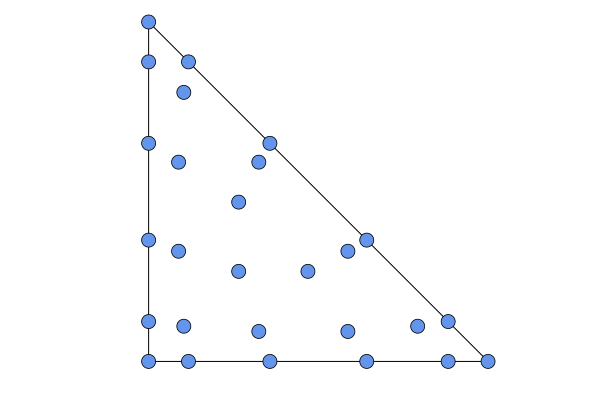
SBP{Hicken}: degree2Naccurate quadrature rules withN+2Lobatto nodes on each face. Nodes forN=4:
Tensor product RefElemData on wedge elements
This is an experimental feature and may change in future releases.
There is experimental support for RefElemDatas created from tensor products of triangular and 1D RefElemData objects.
line = RefElemData(Line(), N_line)
tri = RefElemData(Tri(), N_tri)
rd = RefElemData(Wedge(), TensorProductWedge(tri, line))This new rd::RefElemData can then be used to create a wedge-based MeshData. The individual RefElemData objects can be accessed from rd.approximation_type::TensorProductWedge.